Children Dentistry
Fluoride | Sealants
A child's first visit to the dentist should be enjoyable. Children are not born with a natural fear of the dentist, but they can fear the unknown. Our office makes a special effort to use pleasant, non-frightening, simple words to describe each treatment. We want you and your child to feel at ease from the moment your family arrives at our office. The more you and your child know about the first visit, the better you will feel.
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends...
Children should visit the dentist by their first birthday. It is important that your child's newly-erupted teeth (erupting at six and 12 months of age) receive proper dental care and benefit from proper oral hygiene habits right from the beginning.
Getting to know your teeth is fun!
Download our Dynamite Dental Fun Kit!
When New Teeth Arrive
Your child's first primary or baby teeth will begin to erupt between the ages of six and 12 months, and will continue to erupt until about age three. During this time, your child's gums may feel tender and sore. To help alleviate this discomfort, we recommend that you soothe the gums by rubbing a clean finger or a cool, wet cloth across them. You may also choose to make use of a teething ring. When your child has finished teething, you can expect a total of 20 primary teeth.
Your child's primary teeth are shed at various times throughout childhood. Permanent teeth begin erupting at age six, and continue until age 21. Adults have 28 permanent teeth (32, including wisdom teeth).
Adopting Healthy Oral Hygiene Habits
As your child's teeth erupt, be sure to examine them every two weeks, looking for lines and discoloration that may be caused by decay. Remember that sugary foods and liquids can attack a new tooth, so take care that your child brushes after feeding or eating. We recommend brushing four times a day for optimal oral hygiene: after breakfast, after lunch, after dinner, and at bedtime.
Brushing can be fun, and your child should brush as soon as the first tooth arrives. When a baby's tooth erupts, parents should brush the tooth with a soft-bristled toothbrush and a pea-sized amount of toothpaste. For children younger than two, do not use fluoride toothpaste unless advised to do so by your dentist or other healthcare professional. We suggest reviewing proper tooth brushing procedures with your child.
Flossing is also a part of good oral hygiene habits, and your doctor will discuss with you the right time to start flossing. If you notice signs of decay, contact your dentist immediately.
Preventing Tooth Decay with Regular Checkups
Tooth decay is caused by sugars left in your mouth that turn into an acid, which can break down your teeth. Children are at high risk for tooth decay for a simple reason: many children and adolescents do not practice regular, good oral hygiene habits. Proper brushing and flossing routines combined with regular dental visits help keep tooth decay away.
Your child should visit the dentist every six months for regular dental cleanings and checkups. We recommend fluoride treatments twice a year along with cleanings to keep teeth their strongest. Tooth sealants are also recommended because they "seal" the deep grooves in your child's teeth, preventing decay from forming in these hard-to-reach areas. Sealants last for several years, but will be monitored at your child's regular checkups.
Fluoride
Your child brushes her teeth twice a day, flosses regularly, and visits the dentist every six months. But did you know that rinsing with fluoride – a mineral that helps prevent cavities and tooth decay – also helps keep her teeth healthy and strong?
Fluoride is effective in preventing cavities and tooth decay by coating teeth and preventing plaque from building up and hardening on the tooth's surface.
Fluoride comes in two varieties, systemic and topical:
- Systemic fluoride is ingested, usually through a public water supply. While teeth are forming under the gums, the fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it stronger and more resistant to cavities.
- Fluoride can also be applied topically to help prevent caries (cavities) on teeth present in the mouth. It is delivered through toothpaste, mouthwash, and professional fluoride applications. Professional application of topical fluoride foam and varnishes is also a valuable tool in cavity prevention.
Receiving a fluoride treatment from your dentist
A fluoride treatment in the dentist's office takes just a few minutes. After the treatment, patients may be asked to not rinse, eat, or drink for at least 30 minutes in order to allow the teeth to absorb the fluoride. Depending on your child's oral health or your doctor's recommendation, your child may be required to have a fluoride treatment every three, six, or 12 months. Your doctor may also prescribe at-home fluoride products such as mouthwash, gels, or antibacterial rinses.
How to choose the right fluoride treatment
When choosing an at-home fluoride product (such as toothpaste or mouthwash), always check for the American Dental Association's (ADA) seal of acceptance. Products marked with the ADA seal of approval have been carefully examined and approved by the ADA based on safety and effectiveness.
Sealants
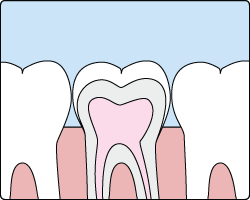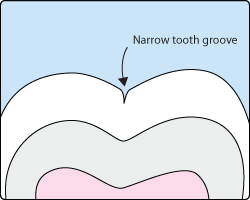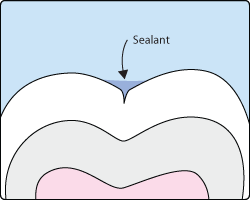
Sometimes brushing is not enough, especially when it comes to those hard-to-reach spots in your child's mouth. It is difficult for a toothbrush to reach between the small cracks and grooves on teeth. If left alone, those tiny areas can develop tooth decay. Sealants give your child's teeth extra protection against decay and help prevent cavities.
Dental sealants are plastic resins that bond and harden in the deep grooves on the tooth's surface. When a tooth is sealed, the tiny grooves become smooth, and are less likely to harbor plaque. With sealants, brushing becomes easier and more effective against tooth decay.
Sealants are typically applied to children's teeth after their permanent teeth have erupted as a preventive measure against tooth decay. It is more common to seal “permanent” teeth rather than “baby” teeth, but every patient has unique needs, and the dentist will recommend sealants on a case-by-case basis.
Sealants last from three to five years, although it is fairly common to see adults with sealants still intact from childhood. A dental sealant only provides protection when it is fully intact so if your child's sealants come off, let the dentist know, and schedule an appointment for your child's teeth to be re-sealed.